Financial Analysis – Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow
Balance Sheets, Income Statements, Cash Flow Statements
There are two types of cash flow statements:
-
Accounting cash flow statements
-
Reconciles the change in the cash account
-
Uses income statement and balance sheets
-
-
Financial cash flow
-
Separates the financing decision form the investment decision
-
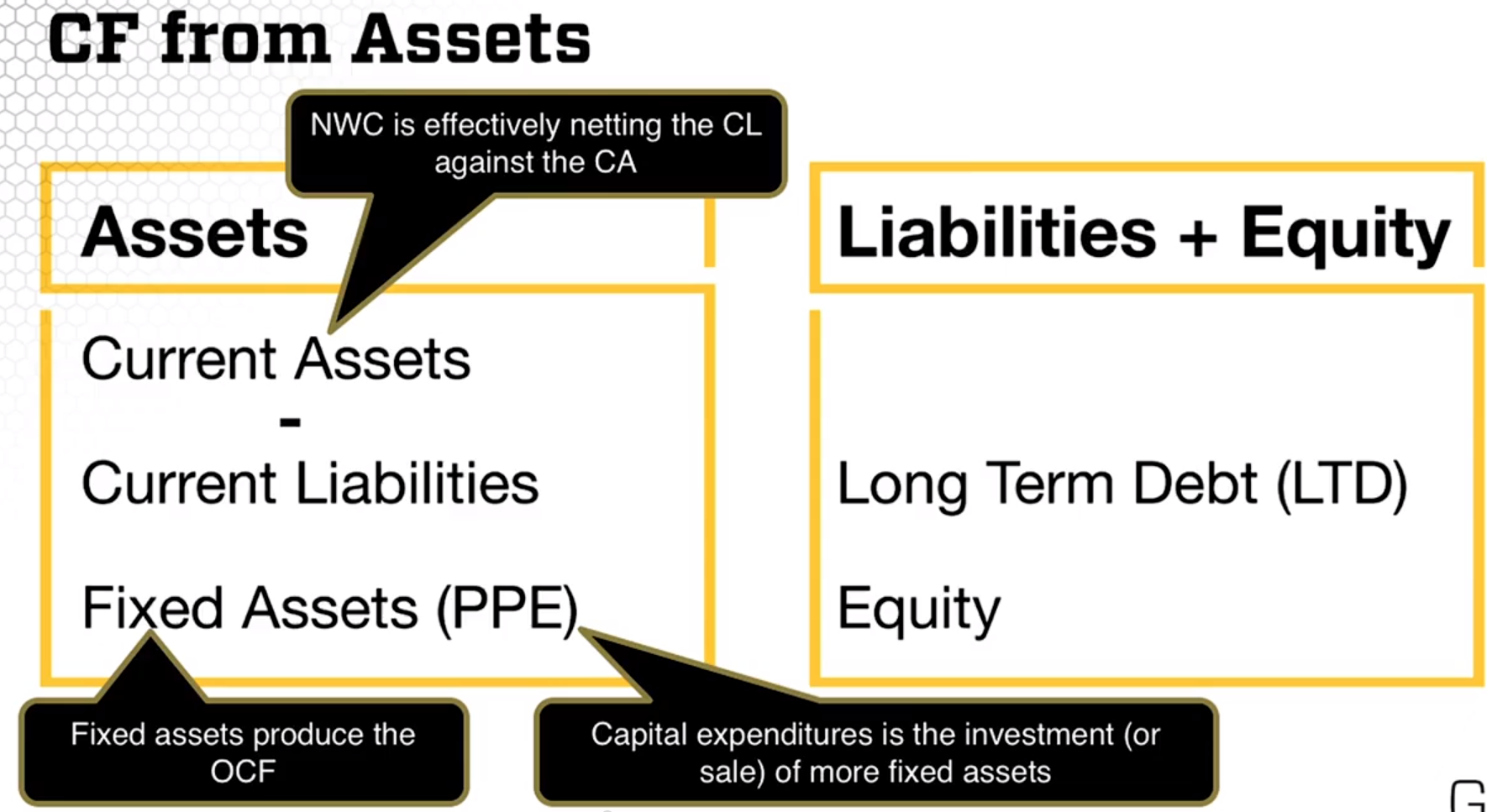
Cash flow FROM assets
- Investment decision
-
Cash flow TO bond/debt holders and stock/equity holders
- Financing decision
-
-
Cash is king when we want to get the value or the price of something
Income Statement
Follow the accrual method of accounting, income and expenses are recorded in the period that they occurred not in the period cash was received or paid. Remember that income statement does not record the purchase of a fix asset, it records the depreciation expenses, related to the useful life of the asset.
Balance Sheet
It is considered a stock statement. A snapshot of what we have. It is organized in terms of liquidity. Accumulated depreciation is a running total of the individual years worth of depreciation. It is a counter account in the assets column. Liabilities are listed in order of maturity. Accrued expenses, examples is salaries, not paid yet.
Equities:
-
Preferred stock
-
Common stock
-
Common stock ( $1 par value) - external equity
-
Capital surplus – external equity -also known as additional paid in capital. Money paid by investors in excess of par value. If stock sold a $20 but par value at $1 then register $19 difference here.
-
-
Accumulated retained earning
- Not paid in dividends
-
Less Treasury stock
- Counter account , for example when the company re-purchases stock. Buy back stock
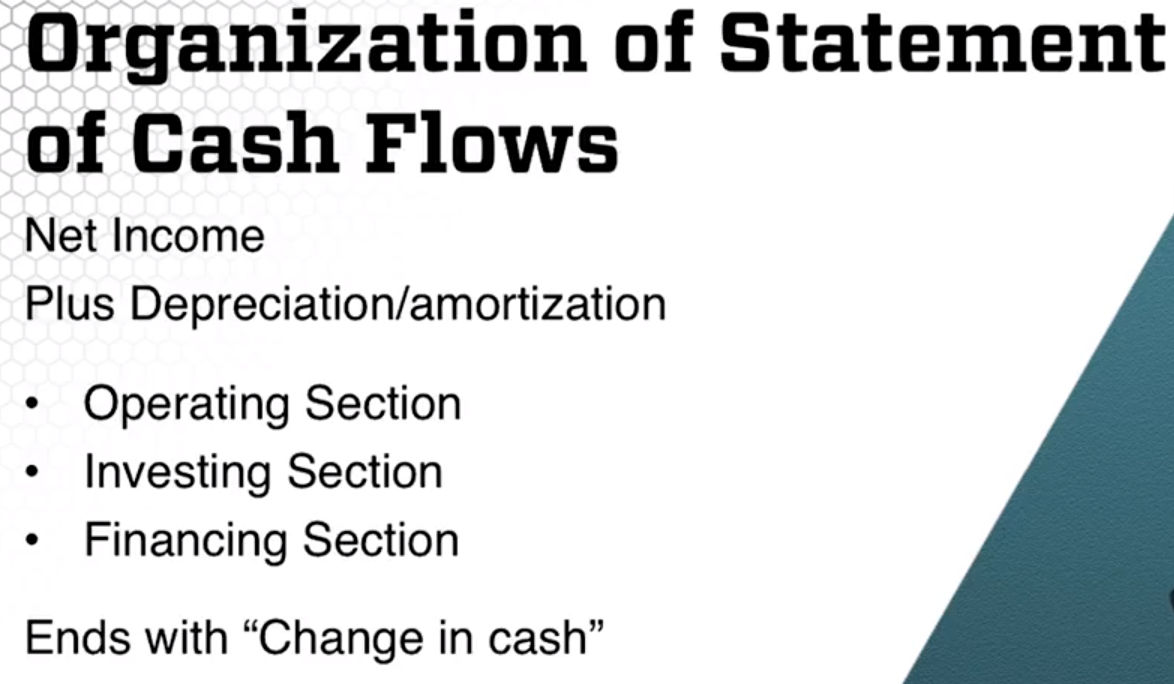
Statement of Cash Flows
- Example of Flow statement. It shows the sources and uses of cash used by a firm
Impact on cash base on this table:
-
If assets increases cash goes down
-
I assets decrease cash goes up
-
If liabilities or equity increase cash goes up
-
If liabilities or equity decrease cash goes down
The statement of cash flows will have the change between the two years
-
The Total CF from operating activities include net income, depreciation expenses, increase in deferred taxes and the Operating section.
-
For the finance section. Dividends = Net Income – Change in Retained Earnings
-
The Proceeds from stock issuance = Change in Common stock + Change Capital surplus. This account shows the stock sold.
-
Purchase of stock = Change in less treasury stock / buy back stock
-
The sum of total for operating, investing and financing, has to be equal to the change of cash between year in the balance sheet.
Financial Cash Flows
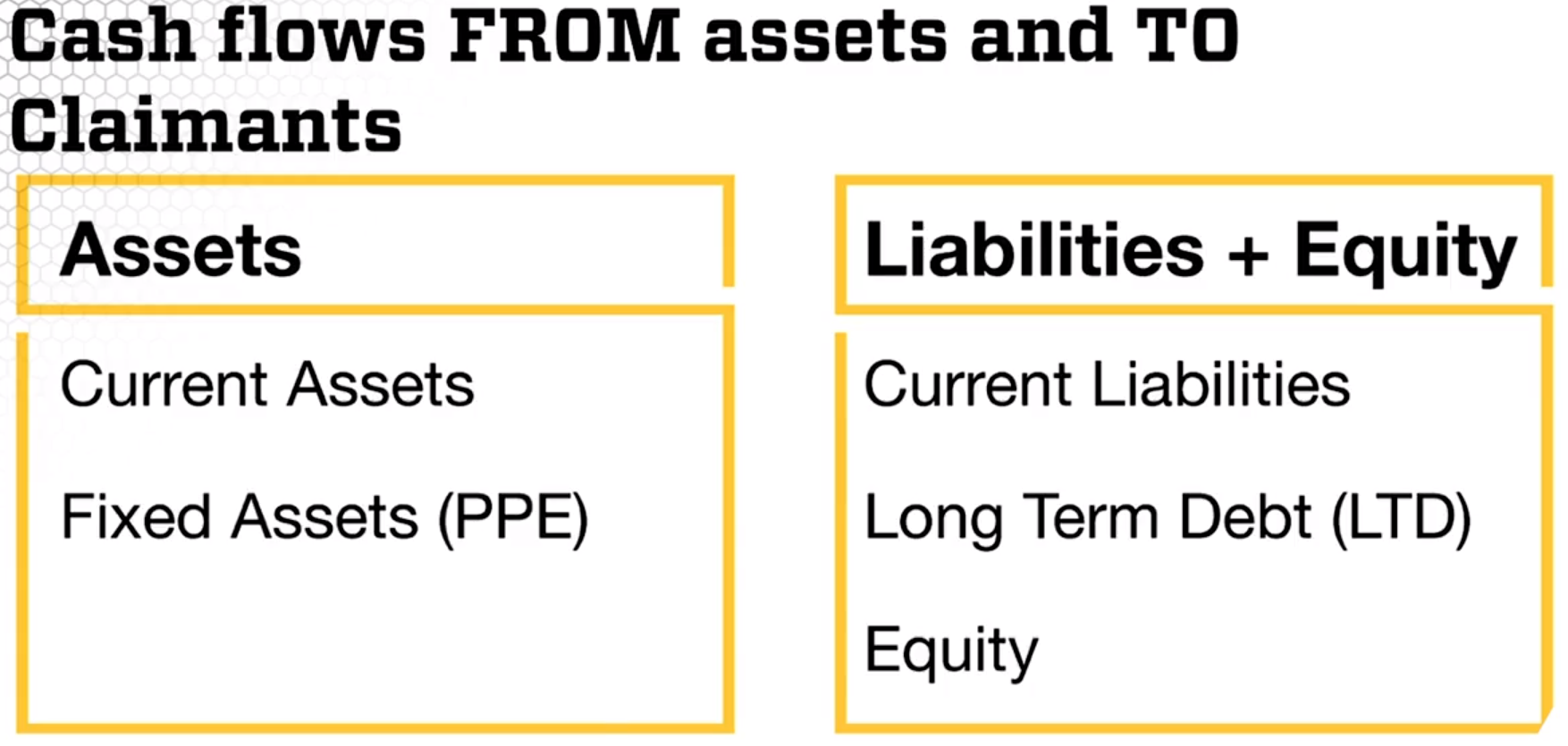
It starts as follows:
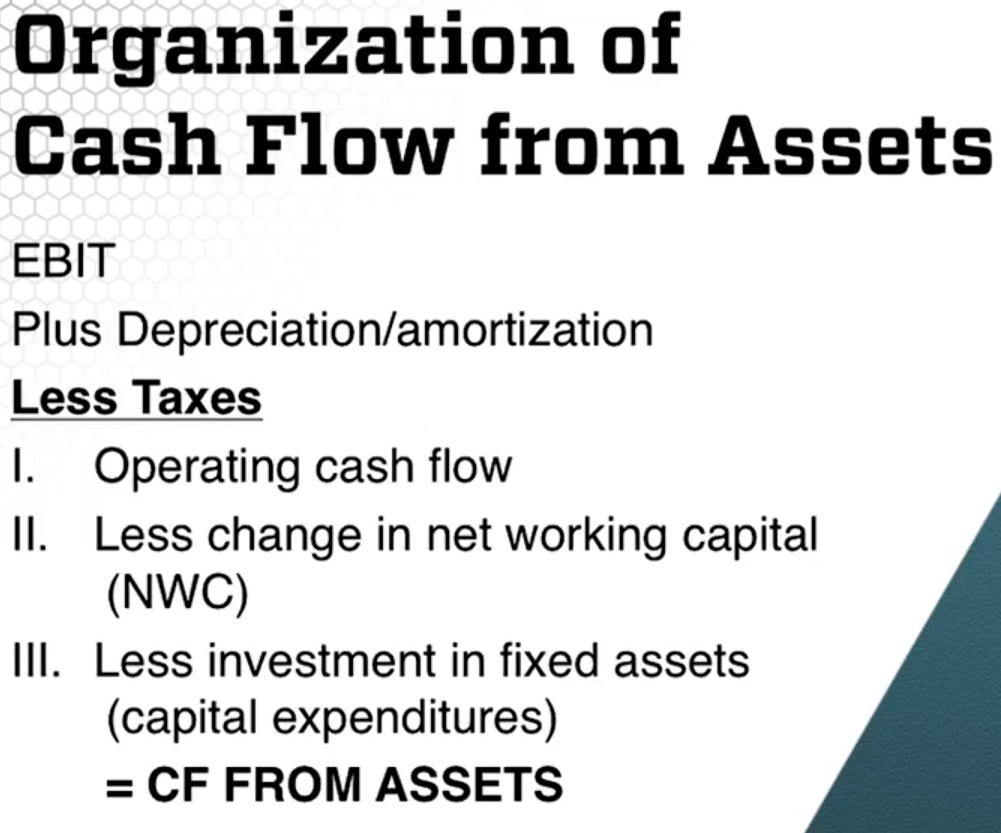
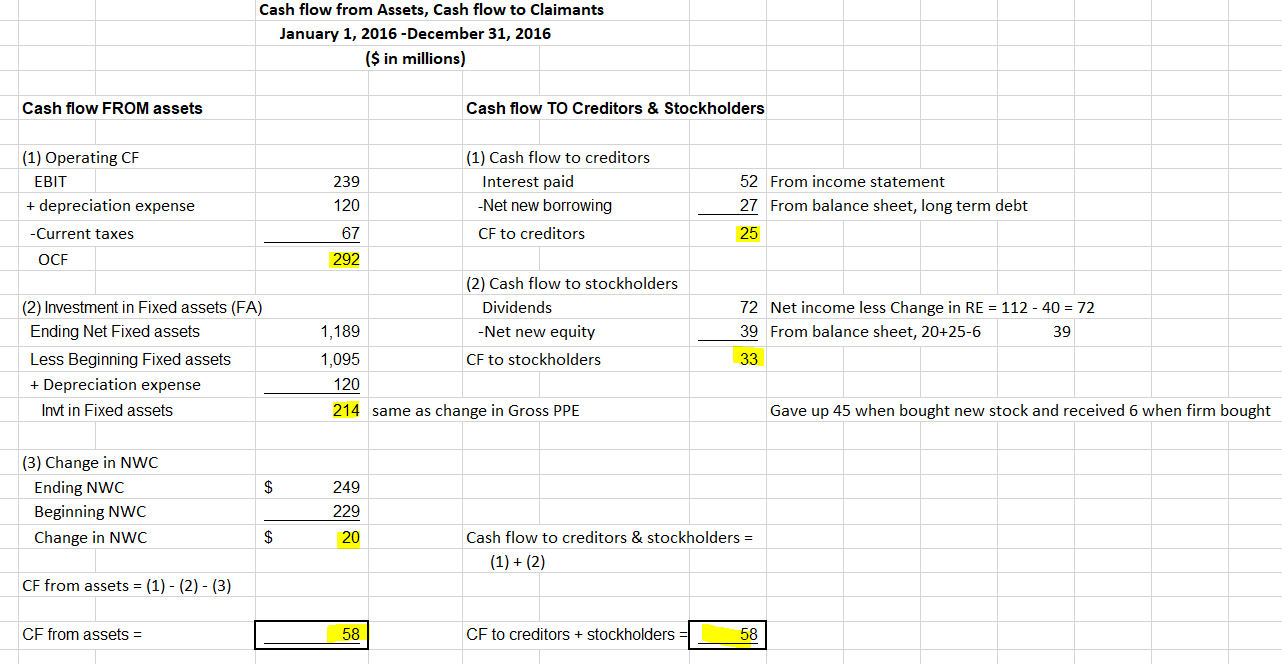
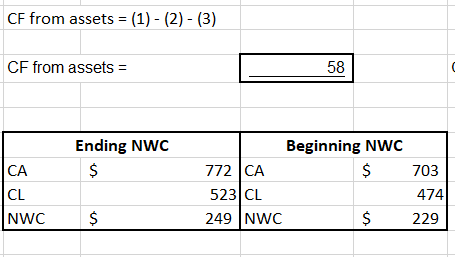
The following shows Cash Flow from Assets: Net Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities . OCF= Operating Cash Flow
Remember the claimants own the assets. The assets produced $58MM
Cash Flow to Debtholders

If net new borrowing was negative, that will be an inflow to the creditors, the “-“ sign takes care is it is an inflow or an outflow
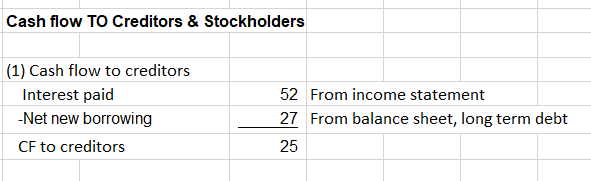
Cash flow to equity holders

For this example: